Calling Sequence
y = besseli(alpha,x [,ice]) y = besselj(alpha,x [,ice]) y = besselk(alpha,x [,ice]) y = bessely(alpha,x [,ice]) y = besselh(alpha,x) y = besselh(alpha,K,x [,ice])
Parameters
- x
real or complex vector.
- alpha
real vector
- ice
integer flag, with default value 0
- K
integer, with possible values 1 or 2, the Hankel function type.
Description
Warning: the semantics of these functions changes between Scilab-3.0 and Scilab-3.1. The old semantics is available for compatibility using the oldbesseli, oldbesselj, oldbesselk, oldbessely functions.
besseli(alpha,x)computes modified Bessel functions of the first kind (I sub alpha), for real orderalphaand argumentx.besseli(alpha,x,1)computesbesseli(alpha,x).*exp(-abs(real(x))).besselj(alpha,x)computes Bessel functions of the first kind (J sub alpha), for real orderalphaand argumentx.besselj(alpha,x,1)computesbesselj(alpha,x).*exp(-abs(imag(x))).besselk(alpha,x)computes modified Bessel functions of the second kind (K sub alpha), for real orderalphaand argumentx.besselk(alpha,x,1)computesbesselk(alpha,x).*exp(x).bessely(alpha,x)computes Bessel functions of the second kind (Y sub alpha), for real orderalphaand argumentx.bessely(alpha,x,1)computesbessely(alpha,x).*exp(-abs(imag(x))).besselh(alpha [,K] ,x)computes Bessel functions of the third kind (Hankel function H1 or H2 depending onK), for real orderalphaand argumentx. If omittedKis supposed to be equal to 1.besselh(alpha,1,x,1)computesbesselh(alpha,1,x).*exp(-%i*x)andbesselh(alpha,2,x,1)computesbesselh(alpha,2,x).*exp(%i*x)
Remarks
If alpha and x are arrays of
the same size, the result y is also that size. If
either input is a scalar, it is expanded to the other input's size. If one
input is a row vector and the other is a column vector, the
resulty is a two-dimensional table of function
values.
Y_alpha and J_alpha Bessel functions are 2 independant solutions of the Bessel 's differential equation :
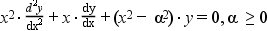
K_alpha and I_alpha modified Bessel functions are 2 independant solutions of the modified Bessel 's differential equation :
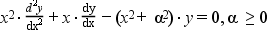
H^1_alpha and H^2_alpha, the Hankel functions of first and second kind, are linear linear combinations of Bessel functions of the first and second kinds:
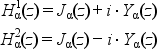
Examples
// besselI functions
// ==================
x = linspace(0.01,10,5000)';
clf()
subplot(2,1,1)
plot2d(x,besseli(0:4,x), style=2:6)
legend('I'+string(0:4),2);
xtitle("Some modified Bessel functions of the first kind")
subplot(2,1,2)
plot2d(x,besseli(0:4,x,1), style=2:6)
legend('I'+string(0:4),1);
xtitle("Some modified scaled Bessel functions of the first kind")
// besselJ functions
// =================
x = linspace(0,40,5000)';
clf()
plot2d(x,besselj(0:4,x), style=2:6, leg="J0@J1@J2@J3@J4")
legend('I'+string(0:4),1);
xtitle("Some Bessel functions of the first kind")
// use the fact that J_(1/2)(x) = sqrt(2/(x pi)) sin(x)
// to compare the algorithm of besselj(0.5,x) with a more direct formula
x = linspace(0.1,40,5000)';
y1 = besselj(0.5, x);
y2 = sqrt(2 ./(%pi*x)).*sin(x);
er = abs((y1-y2)./y2);
ind = find(er > 0 & y2 ~= 0);
clf()
subplot(2,1,1)
plot2d(x,y1,style=2)
xtitle("besselj(0.5,x)")
subplot(2,1,2)
plot2d(x(ind), er(ind), style=2, logflag="nl")
xtitle("relative error between 2 formulae for besselj(0.5,x)")
// besselK functions
// =================
x = linspace(0.01,10,5000)';
clf()
subplot(2,1,1)
plot2d(x,besselk(0:4,x), style=0:4, rect=[0,0,6,10])
legend('K'+string(0:4),1);
xtitle("Some modified Bessel functions of the second kind")
subplot(2,1,2)
plot2d(x,besselk(0:4,x,1), style=0:4, rect=[0,0,6,10])
legend('K'+string(0:4),1);
xtitle("Some modified scaled Bessel functions of the second kind")
// besselY functions
// =================
x = linspace(0.1,40,5000)'; // Y Bessel functions are unbounded for x -> 0+
clf()
plot2d(x,bessely(0:4,x), style=0:4, rect=[0,-1.5,40,0.6])
legend('Y'+string(0:4),4);
xtitle("Some Bessel functions of the second kind")
// besselH functions
// =================
x=-4:0.025:2; y=-1.5:0.025:1.5;
[X,Y] = ndgrid(x,y);
H = besselh(0,1,X+%i*Y);
clf();f=gcf();
xset("fpf"," ")
f.color_map=jetcolormap(16);
contour2d(x,y,abs(H),0.2:0.2:3.2,strf="034",rect=[-4,-1.5,3,1.5])
legends(string(0.2:0.2:3.2),1:16,"ur")
xtitle("Level curves of |H1(0,z)|")
Used Functions
The source codes can be found in SCI/modules/special_functions/src/fortran/slatec and SCI/modules/special_functions/src/fortran
Slatec : dbesi.f, zbesi.f, dbesj.f, zbesj.f, dbesk.f, zbesk.f, dbesy.f, zbesy.f, zbesh.f
Drivers to extend definition area (Serge Steer INRIA): dbesig.f, zbesig.f, dbesjg.f, zbesjg.f, dbeskg.f, zbeskg.f, dbesyg.f, zbesyg.f, zbeshg.f