Name
beta — beta function
Calling Sequence
z = beta(x,y)
Parameters
- x, y
2 positive reals or 2 matrices (or vectors) of positive reals of same size.
- z
a real or a matrix of the same size than
xwithz(i,j) = beta(x(i,j),y(i,j)).
Description
Computes the complete beta function :
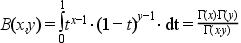
For small x and y the
algorithm uses the expression in function of the gamma function, else it
applies the exponential function onto the result of the
betaln function provided with the DCDFLIB: Library of
Fortran Routines for Cumulative Distribution Functions, Inverses, and
Other Parameter (see cdfbet for more
information about DCDFLIB).
Examples
// example 1 :
beta(5,2) - beta(2,5) // symetry (must be exactly 0)
beta(0.5,0.5) // exact value is pi
// example 2 : an error study based on the relation B(1,x) = 1/x
// (computing 1/x must lead to only a relative error of eps_m, so
// it may be used near as a reference to evaluate the error in B(1,x))
x = logspace(-8,8,20000)';
e = beta(ones(x),x) - (1)./x;
er = abs(e) .* x;
ind = find(er ~= 0);
eps = ones(x(ind))*number_properties("eps");
clf()
plot2d(x(ind),[er(ind) eps 2*eps],style=[1 2 3],logflag="ll",leg="er@eps_m@2 eps_m")
xtitle("approximate relative error in computing beta(1,x)")
xselect()
// example 3 : plotting the beta function
t = linspace(0.2,10,60);
X = t'*ones(t); Y = ones(t')*t;
Z = beta(X,Y);
clf()
plot3d(t, t, Z, flag=[2 4 4], leg="x@y@z", alpha=75, theta=30)
xtitle("The beta function on [0.2,10]x[0.2,10]")
xselect()