Name
cspect — two sided cross-spectral estimate between 2 discrete time signals using the correlation method
Calling Sequence
[sm [,cwp]]=cspect(nlags,npoints,wtype,x [,y] [,wpar])
[sm [,cwp]]=cspect(nlags,npoints,wtype,nx [,ny] [,wpar])
Parameters
- x
vector, the data of the first signal.
- y
vector, the data of the second signal. If
yis omitted it is supposed to be equal tox(auto-correlation). If it is present, it must have the same numer of element thanx.- nx
a scalar : the number of points in the
xsignal. In this case the segments of the x signal are loaded by a user defined function namedgetx(see below).- ny
a scalar : the number of points in the
ysignal. In this case the segments of theysignal are loaded by a user defined function namedgety(see below). If presentnymust be equal tonx.- nlags
number of correlation lags (positive integer)
- npoints
number of transform points (positive integer)
- wtype
The window type
're': rectangular'tr': triangular'hm': Hamming'hn': Hanning'kr': Kaiser,in this case the wpar argument must be given'ch': Chebyshev, in this case the wpar argument must be given
- wpar
optional parameters for
Kaiser and Chebyshev windows:'kr':
wpar must be a strictly positive number'ch':
wparmust be a 2 element vector[main_lobe_width,side_lobe_height]with0<main_lobe_width<.5, andside_lobe_height>0
- sm
The power spectral estimate in the interval
[0,1]of the normalized frequencies. It is a row array of sizenpoints. The array is real in case of auto-correlation and complex in case of cross-correlation.- cwp
the unspecified Chebyshev window parameter in case of Chebyshev windowing, or an empty matrix.
Description
Computes the cross-spectrum estimate of two signals
x and y if both are given and the
auto-spectral estimate of x otherwise. Spectral
estimate obtained using the correlation method.
The cross spectrum of two signal x and y is defined to be
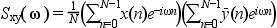
The correlation method calculates the spectral estimate as the Fourier transform of a modified estimate of the auto/cross correlation function. This auto/cross correlation modified estimate consist of repeatedly calculating estimates of the autocorrelation function from overlapping sub-segments if the data, and then averaging these estimates to obtain the result.
The number of points of the window is
2*nlags-1.
For batch processing, the x and
y data may be read segment by segment using the
getx and gety user defined
functions. These functions have the following calling sequence:
xk=getx(ns,offset) and
yk=gety(ns,offset) where ns is the
segment size and offset is the index of the first
element of the segment in the full signal.
Reference
Oppenheim, A.V., and R.W. Schafer. Discrete-Time Signal Processing, Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice-Hall, 1999
Examples
rand('normal');rand('seed',0);
x=rand(1:1024-33+1);
//make low-pass filter with eqfir
nf=33;bedge=[0 .1;.125 .5];des=[1 0];wate=[1 1];
h=eqfir(nf,bedge,des,wate);
//filter white data to obtain colored data
h1=[h 0*ones(1:maxi(size(x))-1)];
x1=[x 0*ones(1:maxi(size(h))-1)];
hf=fft(h1,-1); xf=fft(x1,-1);yf=hf.*xf;y=real(fft(yf,1));
sm=cspect(100,200,'tr',y);
smsize=maxi(size(sm));fr=(1:smsize)/smsize;
plot(fr,log(sm))